Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
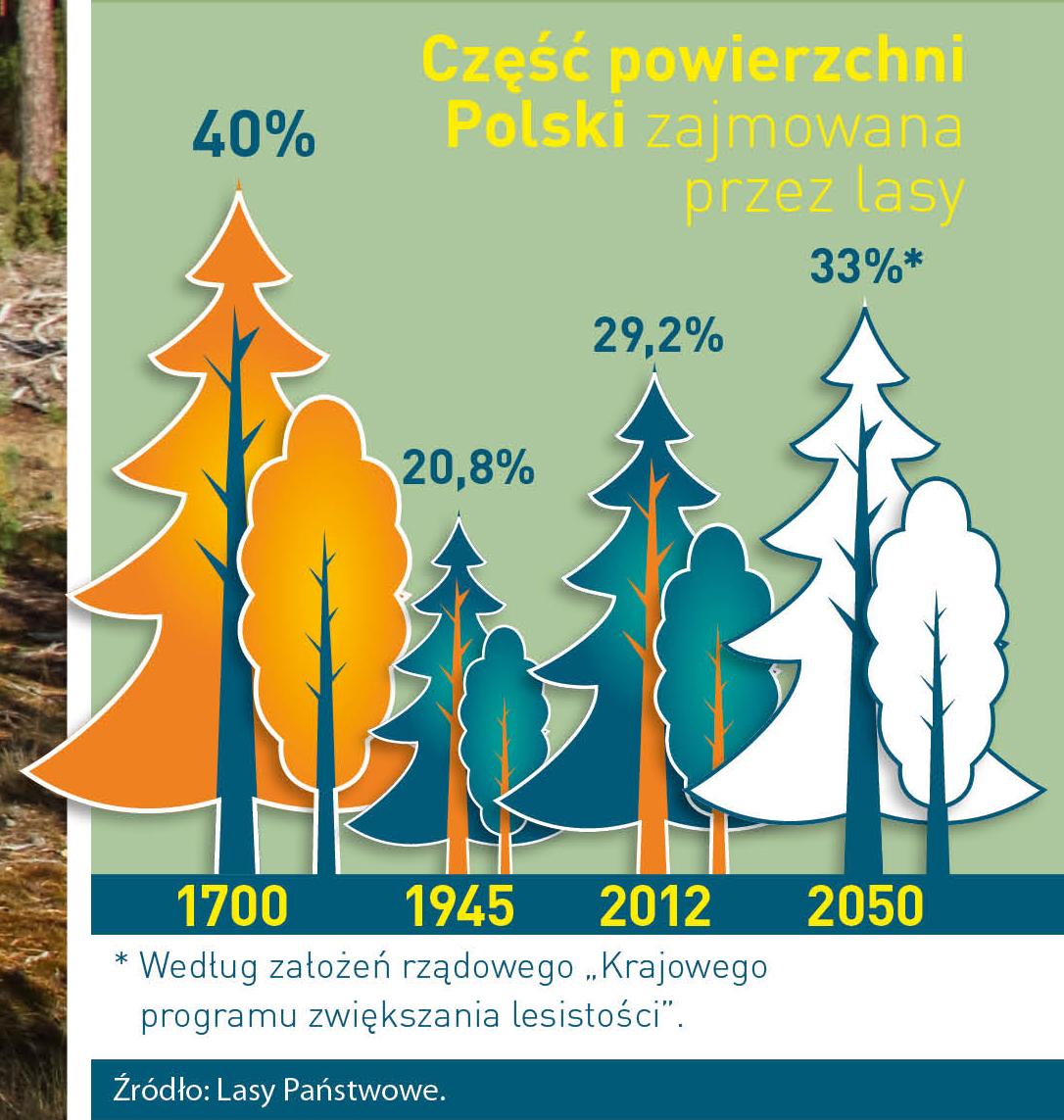
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Kompleksowy projekt ochrony gatunków i siedlisk przyrodniczych na obszarach zarządzanych przez PGL Lasy Państwowe
Kompleksowy projekt ochrony gatunków i siedlisk przyrodniczych na obszarach zarządzanych przez PGL Lasy Państwowe
Nazwa projektu: „Kompleksowy projekt ochrony gatunków i siedlisk przyrodniczych na obszarach zarządzanych przez PGL Lasy Państwowe"
Planowany okres realizacji: 2017-2023
Beneficjent: Państwowe Gospodarstwo Leśne Lasy Państwowe
Cel projektu: poprawa stanu ochrony siedlisk przyrodniczych oraz gatunków roślin i zwierząt, występujących na obszarach Natura 2000, leżących na gruntach zarządzanych przez Lasy Państwowe.
Cele szczegółowe: polepszenie lub przywrócenie właściwych warunków siedliskowych, zabezpieczenie ostoi występowania i miejsc rozrodu populacji zagrożonych gatunków oraz redukcja zagrożeń, ograniczenie rozprzestrzeniania się obcych gatunków inwazyjnych.
Zakres projektu obejmuje wykonywanie działań – najlepszych praktyk w ochronie gatunków i siedlisk, zgodnie z zapisami planów zadań ochronnych, planów ochrony oraz planów urządzenia lasu sporządzonych dla obszarów Natura 2000.
Bezpośrednim efektem realizacji projektu będzie przeprowadzenie działań ochrony czynnej na ponad 90 obszarach Natura 2000, a przez to wsparcie ponad 30 typów siedlisk przyrodniczych i ponad 30 chronionych gatunków.
Wartość projektu
Całkowity koszt realizacji projektu wynosi 33 220 366,48 zł
Maksymalna kwota wydatków kwalifikowalnych wynosi 23 206 997,57 zł
Maksymalna kwota dofinansowania z funduszy europejskich wynosi 19 725 947,92 zł
Na terenie Nadleśnictwa Legnica projekt będzie realizowany na pow. 32 ha
Nadleśnictwo Legnica będzie wykonywało zadanie nr 2 polegające na wykaszaniu powierzchni oraz usuwaniu nalotu drzew i krzewów na siedliskach przyrodniczych 6440 i 6510 zlokalizowanych na OZW Łęgi Odrzańskie PLH020018.
Film o projekcie ochrony gatunków i siedlisk przyrodniczych (OPL)


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański